Women who do excessive drinking are at greater risk. CDC suggests excessive alcohol use among women is risks to women’s health. According to the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance system data, it is reported that at least 40 % of adult women in the last 30 days were involved in drinking alcohol and at least 12 % of them were involved in binge drinking. [1] U.S dietary guidelines suggest that only one drink of alcohol per day must be consumed by women. Alcohol misuse by women can increase the chance of facing higher risks. [2] One of the reasons stated by National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism is that if a woman who weighs the same as man drink the same amount of alcohol, woman’s blood alcohol concentration will be higher because women bodies consists have less water compared to men which put women at greater risk. [5] So, what happens next? How does excessive drinking affect women’s health?
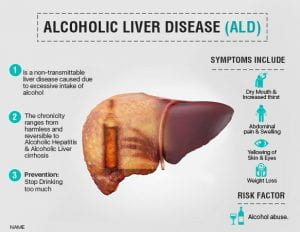
Some of the long-term health risks for women who drink excessive alcohol are as follows: Alcohol use disorder, liver damage, heart disease, brain damage, breast cancer, and fetal alcohol syndrome. [5] Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is the brain disorder it is caused due to the inability to stop drinking alcohol because of emotional and physical dependence on alcohol. Alcohol use disorder ranges from mild to severe. [5] Treatment for AUD includes behavioral therapies and counseling such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational enhancement therapy, martial and family counseling, and brief interventions. Therapies and counseling can help change the behaviors of people who drink excessive alcohol. [3] Liver damage occurs to women as a consequence of drinking excessive alcohol. Treatments for liver damage include alcoholic rehabilitation program, multivitamins such as B-complex vitamins, liver transplant if it is affected by cirrhosis and vitamin A supplements. [8]
Source 1 : https://www.ailbsindia.com/alcoholic-liver-disease-symptoms-treatment/
Heart disease is caused by long-term, excessive and heavy drinking. Women are more likely to experience alcohol-related heart problems than men. Intake of excessive alcohol increases blood pressure which one of the risk factors for getting a stroke or heart attack. Excessive drinking can also make heart muscle weak which can cause heart failure and die. [6] Alcohol also affects the brain; it can also cause brain damage. Based on research alcohol misuse causes more brain damage to women than men because of their body size. Excessive consumption of alcohol directly affects the brain’s neurons and alcohol can damage or kill neurons. There is no treatment for alcohol-related brain damage. [4] Studies show that consuming alcohol can also lead to breast cancer. According to the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, women who take one drink a day have a 5-9 % higher chance of developing a risk of breast cancer than the women who don’t consume alcohol. [5]
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is caused by heavy drinking during pregnancy. Drinking during pregnancy can be harmful, it can interrupt the normal development of the brain and the face. It can also cause cognitive, behavioral, and physical problems in children. Interventions for FASD include school-based interventions, this can help children learn easily. Family support classes and groups help parents on taking care of child with FASD. Behavioral interventions for FASD children include training in problem-solving, personal safety, and personal safety. [7]
Source 2: https://eu.clipdealer.com/vector/media/A:97523658
References
1) Fact Sheets – Excessive Alcohol Use and Risks to Women’s Health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 7, 2016. https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/resources/publications/factsheets/alcohol.htm
2) U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. Appendix 9: Alcohol. 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. Eighth Edition. December 2015. Available at https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/guidelines.
3) “Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) Treatment.” MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 17 Apr. 2020, medlineplus.gov/alcoholusedisorderaudtreatment.html.
4) “Alcohol-Related Brain Damage.” Alcohol Rehab Guide, 8 Oct. 2019, www.alcoholrehabguide.org/resources/medical-conditions/alcohol-related-brain-damage/.
5) Women and Alcohol. (2020, February 24). Retrieved from https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/women-and-alcohol
6) Alcohol and heart disease. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.drinkaware.co.uk/alcohol-facts/health-effects-of-alcohol/diseases/alcohol-and-heart-disease
7) Fetal Alcohol Exposure. (2019, December 24). Retrieved from https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/fetal-alcohol-exposure
8) Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. (2017, April 18). Retrieved from
https://www.healthline.com/health/alcoholism/liver-disease
9) Source: 1 https://www.ailbsindia.com/alcoholic-liver-disease-symptoms-treatment/
10) Source: 2 https://eu.clipdealer.com/vector/media/A:97523658






 Source:
Source: