Authors: Symone Richardson and Christine Nguyen
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, or the NIAAA, binge drinking is defined as an excessive amount of alcohol consumption that increases one’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) to 0.08 g/dl or more (1). For women, binge drinking is typically the consumption of four or more drinks in about two hours. Binge drinking is a serious public health issue that can lead to a lifetime of long-term harmful use of alcohol as well as physical harm such as alcohol poisoning or liver damage. As reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, binge drinking is the deadliest pattern of excessive alcohol use in the U.S. (2). Individuals between the ages of 18 and 34 were reported to be the most likely to binge drink, and compared to their non-college counterparts, young adults ages 18-22 in college are more likely to binge drink. This may be due to social or academic environments of college campuses such as social pressures to drink in order to fit in, the availability of alcohol around campuses, college party culture, or academic related stress. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), in 2018 approximately 11.9 million, or more than a third, of young adults responded as being current binge drinkers (3).
While the number of college students participating in binge drinking has decrease from 45% to 37% between 2003 and 2014, it is still a large problem on college campuses (4). With the global COVID-19 pandemic, these numbers are subject to another shift due to executive orders like social distancing and quarantining. In addition, almost every college campus in America suspended in-person classes early and transitioned to distance learning– with some even cancelling in–person classes for the Fall 2020 semester. Since the COVID-19 pandemic is still ongoing, there has not been a lot of data being produced on the current rates of binge drinking amongst college students during this time of limited interaction. However, we can consider the factors that would lead to the increase or decrease in the percentage of college students binge drinking.
One factor could be access to alcohol. On college campuses, students who are underage may have an easier time getting alcohol, especially in large quantities, from another student or other channels than they would be able to do if they were at home. We have, however, seen that alcohol sales in the United States increased 55% in late March and included online sales and restaurants offering alcoholic beverages for takeout orders (5). 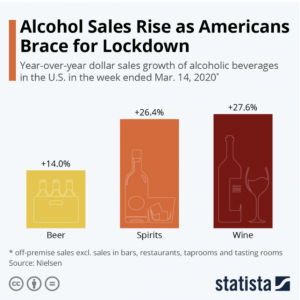
As mentioned earlier, social pressure to drink as part of the college culture will not be as present with students at home or away from college campuses. However, the increased rate of stress and anxiety among college students regarding online learning, isolation from peers, and post-graduate plans in the midst of a pandemic can lead them to drink heavily. Women are affected by stress and anxiety at a higher rate than men with the percentages of having an anxiety disorder being 23.4% and 14.3%, respectively (6). COVID-19 is creating many physical and mental hurdles that everyone, including women and college students, face daily. Unfortunately, alcohol has been a widely used coping mechanism. Women, especially, are more likely to use alcohol consumption to cope with mental health issues like depression and anxiety disorders (7). With all the health effects from alcohol use that disproportionately affect women, it is important to monitor this issue and create interventions that will reduce the burden, especially now in the time of this global pandemic.
References
- Drinking Levels Defined. (2019, November 26). Retrieved from https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/moderate-binge-drinking
- Binge Drinking is a serious but preventable problem of excessive alcohol use. (2019, December 30). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/binge-drinking.htm
- Alcohol Facts and Statistics. (2020, February 18). Retrieved from https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/brochures-and-fact-sheets/alcohol-facts-and-statistics
- College Students Engaging in Less Binge Drinking. (2017, August 3). Retrieved from https://drugfree.org/learn/drug-and-alcohol-news/college-students-engaging-less-binge-drinking/
- COVID-19 drives alcohol sales, raises concerns about substance abuse. (2020, April 14). Retrieved from https://news.usc.edu/168549/covid-19-alcohol-sales-abuse-stress-relapse-usc-experts/
- Any Anxiety Disorder (2017, November). Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/any-anxiety-disorder.shtml
- Stress Drinking: Alcohol Consumption Increases During COVID-19. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://healthcare.utah.edu/the-scope/shows.php?shows=0_p0xim6x3


