Adaptive Reuse: History and Atlanta
Though a recent term, adaptive reuse as a concept dates back to the mid-twentieth century, springing out of the urban planning war being waged by New York urban planners Robert Moses and Jane Jacobs. Evaluating whose core principles of design set forth the best structure for urban planning and policy could easily fill books, much less another built environment analysis, so to simplify matters, this analysis will settle for an admittedly oversimplified view of what both represented.
Moses looked at the city on a larger scale. He was preoccupied with improving traffic, building massive infrastructure projects like highways, bridges, and tunnels. Jacobs, on the other hand, prioritized the small elements of cities: the communities, the culture, history, and other intangible factors. While Moses has undoubtedly left an almost permanent mark on the American map, modern developments like adaptive reuse may have given Jacobs the edge in posterity (Sheir).
(For more information listen to the below episode of Slate’s Placemakers about Moses and Jacobs. Follow this link to go to the podcast home page for more episodes about city planning across the United States, including Atlanta).
As Moses fought for demolition and replacement, Jacobs advocated for repurposing old buildings for new needs. This idea would later be named adaptive reuse (Carswell).
Although it would take until the twenty-first century before adaptive use became a solid and understood concept, examples of it appeared throughout the second half of the twentieth century. Many cite Ghirardelli Square (a former chocolate factory turned shopping center) as the first instance of adaptive, or urban, reuse, the project occurring in the 1960’s. The first wave of adaptive reuse hit New England in the 1980’s. Abandoned mills, relics from a long-ago textile boom, were converted into museums (like the Massachusetts Museum of Contemporary Art) or residential buildings. The beginning of the new century saw large-scale adaptive works capture the public eye in projects like the High Line in New York City. Thus, adaptive reuse has emerged as a prominent principle and strategy in urban design and redevelopment (Carswell; Birge-Liberman).
- Massachusetts Mills Lowell, MA
- Royal Mills West Warwick, RI
- Slater Mill Pawtucket, RI
- Border City Mills Fall River, MA
(All of these apartment buildings were converted from New England textile mills).
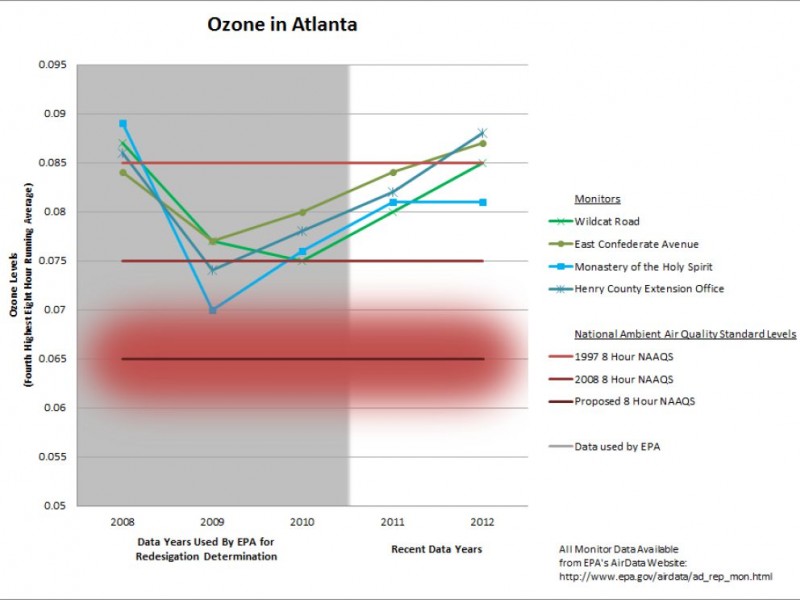
A chart showing pollution levels in Atlanta. The three lines are different estimated levels. The red range underneath is the range that NAAQS considers safe.
The possibilities of adaptive reuse have captured the imaginations of urban citizens across the world; however, it seems to have caught Atlantans even more so. After all, it represents a unique type of hope for a city that has long been dominated by “sprawl” (constant expansion of urban and suburban areas and roads). To demonstrate the sprawling woes of Atlanta, the city has the second highest amount of streets per capita, yet suffers the nation’s fifteenth worse traffic. It is the least densely populated metropolitan area in the country but between the period of 1982 to 1992, Atlanta increased the rate of deforestation by 38% to develop more low-density residential areas, contributing to Georgia’s status as the state with the third highest amount of deforestation. All of these factors have contributed to chronic air and water pollution, Atlanta having been ranked 18 on a list of American cities with the lowest air quality (Kundell and Myszewski). Publications including The New York Times and Politico have consistently labeled Atlanta as the “poster child” for sprawl.
Beyond the environmental and transportation issues lie a long history of demolition and replacement, an absence of redevelopment or adaptation. As just one example, the Civic Center was supposed to be a city marvel, but today it stands useless, devoid of activity as it razed mixed-use structures with parking lots and oversized highways. Before its construction, the site was a community known as Buttermilk Bottoms, populated mostly by African-Americans. The city bulldozed the entire community and replaced it with a building that quickly became obsolete and currently burdens the city more than anything (Pendered). Atlanta Mayor Kasim Reed has worked to redevelop the site into one that focuses on green spaces and mixed-use, but these plans continue to fall through (Allison).
Nevertheless, one project did come along that battled its way into existence and into the hearts of Atlantans: the Beltline. The Beltline, a prime representation of urban reuse, was based off a thesis by Georgia Tech student Ryan Gravel from 1999 that evolved into a proposal for a 33-mile paved trail that aided pedestrians and rail transit using the 22-mile rail corridor that encompasses Atlanta as a foundation. The project has been in development for several years and will continue to be in progress for quite some time, but it has already managed to impress itself upon the city and earn international attention and acclaim (“Atlanta BeltLine Overview”). For a city so long dominated by destruction and sprawl, it welcomed the possibility of a new era focused more on adaptation and sustainability.
Still, I worry that evaluations of urban reuse fail to achieve a holistic review. Most of the people who discuss and think about urban reuse do so because they already support it, producing a constrained viewpoint that struggles to properly assess issues with adaptive reuse and react proactively and sufficiently to them. In the ensuing sections, I will cover why I love adaptive reuse but also provide an overview of some reasons why we need to challenge our support and why the model for making the products of adaptive reuse, and society in general, better might be the companionship of two Supreme Court Justices.
An Adapted Hope
Unarguably, adaptive reuse immediately presents desirable, tangible benefits. As documented in the case of Atlanta, it has a proven track record of transforming desolated, almost dystopian built environments into gorgeous green spaces. Without question, the Atlanta Beltline symbolizes a monumental achievement in aesthetic overhaul, taking parking lots and making them a sculpture gallery (Sharman).
(The above pictures display areas of the Beltline before construction and the below pictures show those same areas after, highlighting the stark transformation).
However, projects like the Beltline can have tangible and powerful benefits outside of mere aesthetics. Research has started to show that green spaces can significantly impact personal and public health. In a myriad of ways, these areas improve personal health, like:

A group of bikers on the Beltline
- They encourage active transportation (walking, biking) that support overall fitness;
- Access to natural spaces helps stress management, especially in children;
- Children tend to exhibit better behavioral habits when they can easily access outdoor spaces;
- Open spaces and trails often lead to people living around them to engage in more active lifestyles;
- Given the ability of green spaces to encourage active lives, they also can reduce obesity rates.
Further, these factors can expand to better the healthiness of the entire city, including:
- Increased active transportation options decrease the overall use of cars, reducing pollutants in a more efficient way;
- Reduced pollution from decreased car usage can lower the prevalence of asthma and lung cancer;
- Urban pollution often disproportionately impact lower and middle classes, so green spaces can contribute to health equity
A quick walk on the Beltline makes this potential abundantly clear. Everywhere you go, bikers and joggers dot the trail, and the sound of panting breath is a permanent background fixture. Atlanta’s design has often rendered exercises like jogging or casual recreation like walking to the store impractical, but the Beltline has started to solve that problem. In Ryan Gravel’s book The Way We Want to Live, he describes the moment that amazed him most during the nascent stages of the Beltline: seeing a woman casually walking to the store (127-137). I had a similar experience shortly before reading that section of the book. All around me bikers and joggers passed, but I could also see residents emerging from direct back entrances onto the Beltline to walk to the store. Such moments establish the Beltline’s ability to influence our lives in simple, quotidian ways, a positive harbinger of adaptive reuse’s future.
And research has also suggested that green spaces can increase social activity, strengthen communities, and reduce cities’ budgets by decreasing infrastructure budgets (Health in the Green Economy: Transport Sector; How Natural and Built Environments Impact Human Health). Of course, the urban environment presents the challenge of finding space to do that, so revitalization projects offer a solution to that problem, taking abandoned spaces and generating a public good. Again, I have seen the Beltline do this. People gather at parks and attend events together. It offers a place for people to leave their homes and interact with others, highlighting one of the keynote characteristics of urban life.
Another feature that many cities strive for is historic preservation. After certain buildings have outlived their uses or origin, many citizens still see a benefit in retaining the foundations of these buildings to preserve the history and culture of the city. Since this process requires that old buildings be repurposed for modern demands, adaptive reuse is a process inextricably tied to historic preservation (Birge-Liberman). After all, the Beltline preserves the foundation of the Atlanta rail corridor, the impetus for settling the city. Or there’s Ponce City Market. Now a hub of shopping and eating, the hulking building was once a warehouse and distribution facility for Sears. The building marked something important to the city’s history, but a building of such a scale offers no obvious service in the modern world. Instead, the city has transformed it into a building that can supply current demands like parking and shopping while maintaining a landmark in Atlanta history (Weible).
(A 360 virtual reality tour of Ponce City Market’s conversion).
Reality Strikes Back?
Sadly, nothing can be truly this idealistic. Despite widespread positives, we still have to consider what problems come out of this policy. Perhaps the biggest critique originates in one of society’s favorite buzzwords: gentrification.

Political cartoon about gentrification
The word has gained lots of connotations and meanings. In fact, Emily Badger of The Washington Post a few years ago denounced the term as emotionally loaded and without real meaning. While I happen to agree with Ms. Badger’s analysis entirely, for convenience sake it makes more sense to use the word under a standard working definition. Thus, I will define gentrification as a consequence of city planning that leads to wealthier, and generally more privileged, people to move into a city and drastically change its culture and raise prices, especially in the housing market (Badcock; Hayes). Regarding Atlanta, several have expressed concerns with how the Beltline might affect rent prices for low-income households already residing near the Beltline. Recently, Atlanta has been recognized as a leading city for gentrification, and the Beltline has been seen as exacerbating that problem (Blau). Just a month ago, Ryan Gravel, the visionary behind the Beltline, resigned from his position on the Beltline board because he worried that the organization was not acting sufficiently to expand and protect affordable housing (Stafford).
Furthermore, it must be considered that urban reuse does not welcome everyone. Many of these old buildings were not built with broad demographics in mind, particularly the disabled. Several of these buildings rely on steep staircases and narrow hallways that give little room for wheelchairs. Or some buildings feature only one bathroom on each floor because the construction did not account for women (the merits of binary bathrooms is a subject for another time). Or, the buildings utilize hazardous or ineffective materials that cannot adequately cater to modern needs (Carswell). The perceived nobility of adaptation may obscure the stark realities that complicate these issues.
Lastly, we must consider what kind of moral relativism much of this analysis relies on. I agree with many writers and professors of mine who advocate for urban reuse. However, other perspectives exist, and though it may seem clear to me or others that historic preservation possesses intrinsic value, not everyone thinks that way. Though I disagree with the philosophy of Objectivism and Ayn Rand firmly, her ideas and similar ones have significant followings that assert that the government has no role to play in preservation or that disagree that preservation is even a positive goal (Cunningham). When evaluating adaptive reuse moving forward, it might be necessary to look at things in an objective or utilitarian prism that prioritizes function or practicality. It may be the colder option, but may be the most realistic one.
(This video introduces the foundations of objectivism. Be cognizant that the video was created by a very pro-Rand group, the Ayn Rand Institute).
How to Make Old Buildings Great Again?

This map shows different developmental areas and factors of the Beltline. The areas covered in orange are areas where property taxes have been increased.
The trap of evaluating urban reuse is often a deceptively simple appeal. For someone who, like myself or my classmates or my professors, has a deep love of preservation and the character of a city and public social good, the virtues of adaptive reuse present themselves clearly, but this can easily obscure our capability of empathizing with other world views and identifying clear disadvantages.
For example, the people whom the Beltline has hurt the most are many of the people who already lived by it. These residents tend to be low-income households and bought the property for its low price. Because of the low property values, the city put high property taxes in the area back in the 90’s. Now, the Beltline is raising property values, and the city has not lowered the property tax for the area; in fact, the tax has increased within a mile of the Beltline, the area most impacted taxwise. Thus, some households have seen their tax burden triple (Immergluck).

A wheelchair user eating at Krog Street Market
On the other hand, some structures have found ways to reconcile the drawbacks of adaptive reuse. Krog Street Market, a mixed-use commercial center converted out of a factory, has gained notoriety for being wheelchair-friendly. Large ramps appear throughout the area, and several stores have low tables and counters plus extra space (Kantor).
So, what does adaptive reuse need more than anything to cement its success? In my opinion, critics. Advocates incomparably outnumber critics, and the inevitable echo chamber that such a balance produces leads to neglect of problems. We need activists, reporters, columnists, and bloggers to stand up and tell us why urban reuse is bad and what is wrong with it. It will make the progress of reuse projects slower, but it will make our communities and institutions better. If a large-scale grassroots organization existed solely to lobby against the Beltline due to gentrification, Beltline planners and supporters might be forced to truly confront the problem and develop actual solutions, not soundbites and fruitless plans.
Until somebody raises hell against the problems that adaptive reuse projects have created, no matter how successful and desirable these projects may be, we, supporters, will not be fully moved to actively and sincerely strive for resolutions. To unleash the true and wonderful potential of urban reuse, first somebody needs to tell us, loudly, why adaptive reuse projects cannot achieve it currently.

Justices Ginsburg and Scalia at the opera. Their unlikely and adorable friendship epitomizes how substantial debate and respect between ideological opposites can strengthen institutions, people, and ideas.
For an allegory, look at the Supreme Court for the past decade. Associate Justices Ruth Bader Ginsburg and the late Antonin Scalia disagreed on nearly every judicial matter, yet they formed a bond over their disagreements. When Ginsbeurg wrote an opinion that Scalia planned to dissent, and vice verse, they would share with each other drafts so that they could critique each other and make their arguments stronger while challenging their beliefs. Us adaptive reuse supporters need our Scalia.
Works Cited
Allison, David. “Weingarten Realty Stops Pursuing Atlanta Civic Center Redevelopment.” Atlanta Business Chronicle. N.p., n.d. Web. 16 Nov. 2016.









